
A Brief History of Data
Data is considered to be one of the most valuable commodities in the world today. It ranks alongside other precious assets such as rare earths, gold, diamonds and oil. Our lives are increasingly bound to the story of data. In the beginning, it was used to enable tribes of humans to survive the winter. Later it became a means of understanding and exercising power. In ancient time we have kings using it to manage the tax take and ownership of land. In modern times we have political campaigns using data to understand and manipulate the voting public.
How has this addiction to data happened? Why has data become so important to us in both our personal and working lives. What is it about data! This book follows the journey data has taken from pre-history in the mid 20,000’s BC and travels through time to the present day.
Buy this book:
A journey through history
Travel from pre history to the Norman conquest, though the black death and then the post war years to eventually end up in the modern day. This book takes you on a journey to discover how the human race has become addicted to the four letter word DATA.

To find out more, scroll further down.
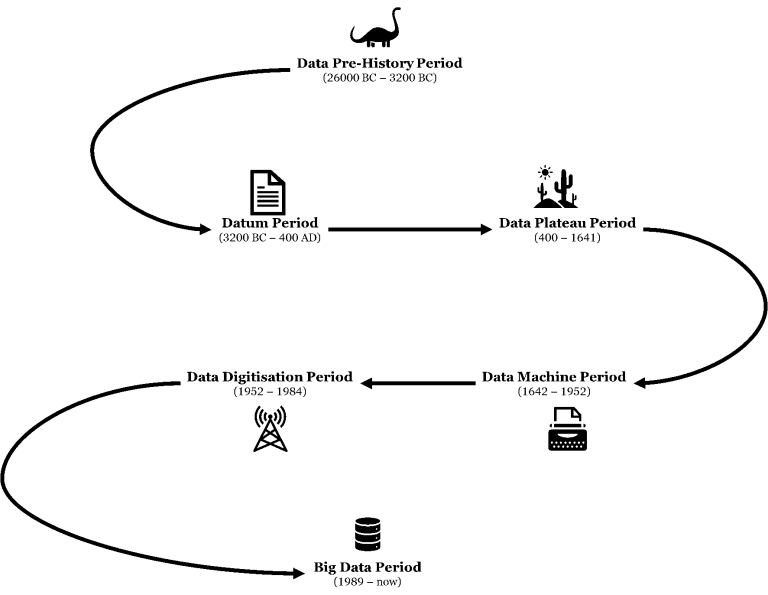
The Timeline for the History of Data
Data Pre-History Period
(26000 BC – 3200 BC)
18,000 BC: The Ishango Bone, Uganda

15,000 BC: Lascaux Cave Paintings, France
4000 BC: Babylonians using census
35-3200 BC: Cuneiform, Mesopotamia
3200 BC: Early Egyptian Hieroglyphs (alphabet of 7-800 hieroglyphs)

Datum Period
(3200 BC – 400 AD)
3000 BC: First libraries in Nile region and Mesopotamia
2500 BC: Egyptians become avid census users
2400 BC: Babylonians using Abacus’s
202 BC – 220 AD: Creation of a number of imperial libraries in China
1050 BC: Phoenician Alphabet originated
1900 BC: Library in Nippur, Egypt
700 BC: Library in Nineveh, Egypt
800 BC: First true alphabet emerged in Greece
1800 BC: Egyptian workers and slaves develop alternative to hieroglyphs

323 BC – 246 BC: Library of Alexandria, opened during reign of either Ptolemy I (323–283 BC) or Ptolemy II (283–246 BC).
213 BC: Mass burning of books in China

612 BC: The Royal Library of Ashurbanipal is destroyed by fire. It was created sometime in the 7th century
300 BC: Late Egyptian Hieroglyphs (alphabet had grown to circa 6,000 hieroglyphs.
30 BC – 48 AD: Romans invaded Egypt and caused significant damage to the Library of Alexandria
2 AD: Population of China had reached 57.67 m
105 AD: Invention of paper by Cai Lun in China

100-200 AD: Greek Antikythera Mechanism in use
135 AD: Construction of the Library of Celsus in Ephesus in modern day Turkey.
240-270 AD: Shapur I built the Academy of Gundeshapur in Persia
4th century: Scrolls being replaced by books within Europe
377 AD: By this time there are 28 libraries in Rome
Data Plateau Period
(400 – 1641)
618 to 907: Book printing in China within the Tang Dynasty used hand carved wood blocks.
10th century: Paper has replaced papyrus in the Islamic world for books.
1041-1048: Bi Sheng invents the pre-formed printing blocks.
1066 AD: Norman invasion of England by William the Conqueror

13th century: Inca Empire formed and the development of the Quipu
1450s: Johannes Gutenberg re-invents Bi Sheng’s pre-formed printing blocks and the printing press.

Data Machine Period
(1642 – 1952)
1662: John Gaunt’s Bills of Mortality is published
18th century: Punch cards used to control textile looms
1832: Semen Korakov using punch cards to store and search information.
1837: Charles Babbage invents the Analytical Engine

1877: Thomas Edison invents the Phonograph
1887: Hollerith won the contract for counting and tabulating the results of the US 1890 census.
1887: First punch card machine working
1890 Magnetic Wire recording invented by Valdemar Poulsen
1924: CTR (Computer-Tabulating-Recording Company) changed its name to IBM
1927 Magnetic Tape invented by Fritz Pfleumer
1932 Magnetic Drum developed
1935 AEG develop the Magnetophon K1 Reel to Reel tape recorder
1943 Simple neural network built using electronic circuits.
1944 First attempt to understand how much data there is in the world (specifically US libraries) is undertaken by Fermont Rider.
Late 1940s Magnetic Core Memory developed
1948 Random Access Memory (RAM) invented
1950 Turing test defined
1951 Isaac Asimov, Foundation published which refers to Pshycohistory which is really data science but under a different name.
1952 The term Machine Learning first used
1951 Isaac Asimov, Foundation published which refers to Pshycohistory which is really data science but under a different name.
Data Digitisation Period
(1952 – 1984)
Mid 1950s: MIT developed the Whirlwind Computer
1956: The founding event for AI the Dartmouth Conference is held and IBM launch the 350 RAMAC which has a Magnetic Hard disk.
1957: The Mark 1 Perceptron created that can recognise images.
More to be added soon, so come back and see how far we have travelled into the journey data has taken through history.
© Copyright. All rights reserved.
We need your consent to load the translations
We use a third-party service to translate the website content that may collect data about your activity. Please review the details in the privacy policy and accept the service to view the translations.